Introducing Arweave’s Tech Ecosystem (Part 3)
This post is based on the speech that outprog, the everFinance’s founder who proposes the SCP (Storage-based Consensus Paradigm) theory, gave on BeWater Live. It is intended to give you the whole picture of Arweave’s tech ecosystem by delving into Arweave, SmartWeave and SCP, as well as the two-layer model that integrates PoW and PoS.
This post is divided into three parts, each of which centers on the following content:
- Why is perpetual storage economically viable
- How does Arweave ensure miners store all the data
- Blockweave technology
- Implicit incentive mechanism
- SmartWeave
- Storage-based Consensus Paradigm
- The Web3 Era of Infinite Scaling
- everPay Architecture
3. The Two-layer model that integrates Permanent Storage and PoS
- The Design of KYVE
- The Design of Koii that Integrates Permanent Storage and Pos
- Conclusion
Part3: The Two-layer model that Integrates Permanent Storage and PoS
This post is the third and final part of “Introducing Arweave’s Tech Ecosystem”.
After the SCP has been iterated and updated for more than half a year, we found that data verification is the core problem of the paradigm. SmartWeave cannot resist DDoS attacks because it fails to handle data verification properly. The validity of on-chain data is of utmost importance. Only when the data is valid and accurate can the usability and scalability of applications be ensured.
In everPay, the coordinator is responsible for data verification, which can be expanded to decentralized solutions.
Decentralized data verification solutions are used by a great number of projects in the Arweave ecosystem. All these projects conform to the SCP. Among them, SmartWeave is a typical example. Other projects built on Arweave, such as publish content platform koii, data archiving protocol KYVE and the oracle solution Redstone, are essentially designed according to the similar SCP model as everPay’s.
1 Design of KYVE
According to KYVE’s architecture, the data is uploaded by the uploader and then voted on by the Validators. KYVE ensures the validity of the data included on-chain and removes any invalid data so that clients do not need to load invalid data.
2 The Koii Design that Integrates Permanent Storage and PoS
Koii has built a fully decentralized consensus network with high scalability. It adds a PoS layer on top of the permanent storage chain Arweave. Only those who stake tokens are qualified to verify data in the Koii network. Any data verification performed by non-stakers are deemed invalid.
If a validator node which has staked tokens broadcasts false data, it’ll get slashed according to Koii’s PoS mechanism. As long as the number of tokens slashed reaches the threshold value, the node will be kicked out of the network. This way, Koii creates a fully decentralized task distributor.
For example, there might be 100 Koii nodes that can deal with simple computation tasks. Similar to the developers who write smart contracts in Solidity, the task distributor provides Koii nodes with task scripts for computation. The nodes that accomplish the tasks can obtain newly created tokens as rewards as long as they include the validated data onto the chain.
In the Koii network that contains 100 validator nodes, it barely requires three or four nodes instead of all the nodes to compete in order to execute a computation task distributed by the developer.
For example, the computation tasks of Application A and Application B can be handled by different nodes in the Koii network. As long as a computation task is done by a single node in the network, it will be computed and verified in an accurate way.
The SCP that integrates permanent storage and PoS has another advantage. The nodes that participate in staking cannot tamper with the computation results of a deterministic program, which means that the consensus is immutable. The consensus depends on a storage blockchain.
As the SCP suggests, a consensus reached on the basis of perpetual storage cannot be tampered with by third parties. Even if barely 1 million dollars of tokens are staked by validator nodes, projects worth 100 million or 1 billion dollars can run properly in the Koii network because staking only offers data verification capabilities instead of basic consensus protection.
Ultimately, a consensus is reached through the SCP. Intuitively, a Koii node is like an accountant who has no access to real assets. This makes it that it can only help accounts, but cannot change the consensus. This model has a great advantage over the traditional PoS mechanism. In the traditional PoS mechanisms, running a project worth 1 billion dollars requires 10 billion dollars worth of tokens to be staked. On the contrary, the PoS mechanism based on the SCP allows projects of great value to run on top of a relatively small number of stakes.
3 Conclusion
To sum up, the hybrid model that combines permanent storage and PoS is a way to build a dApp with the permanent storage chain Arweave as Layer 1 for perpetual storage and the PoS mechanism as Layer 2 on top of it.
The projects built on top of Arweave are not restricted to the DeFi field, but also cover every aspect of Web2. Ardrive is one of the examples. You can pay AR tokens to store an image on it and download the image whenever you need.
To give another example, the oracle solution Redstone aims to upload the validated pricing data to Arweave. Similar to everPay, Koii and KYVE, Redstone is also built with a staking mechanism. It verifies the pricing data of various tokens and stores it in Arweave, so that anyone can obtain accurate crypto prices.
Redstone can be considered as the Chainlink in the Web3 space. It allows all the applications built on the SCP to read the data from a storage blockchain to perform off-chain computations. The data accuracy is ensured by the economic mechanism of Redstone.
Thanks to the hybrid model, all the business programs that perform computations off-chain can offer an optimal user experience and extremely high TPS. Besides, the applications built on the SCP benefit from the characteristics of decentralization, which are,traceability, immutability and trustlessness.
1.资讯内容不构成投资建议,投资者应独立决策并自行承担风险
2.本文版权归属原作所有,仅代表作者本人观点,不代表本站的观点或立场
您可能感兴趣
-
 早报 | 特朗普媒体科技集团 Q3 亏损 5480 万美元;Re7 Labs 发布 xUSD 脱锚事件报告;Michael Saylor 再次发布比特币 Tracker 信息
早报 | 特朗普媒体科技集团 Q3 亏损 5480 万美元;Re7 Labs 发布 xUSD 脱锚事件报告;Michael Saylor 再次发布比特币 Tracker 信息整理:ChainCatcher 重要资讯:特朗普媒体科技集团 Q3 亏损 5480 万美元,目前持有超过 11,500 枚比特币 赵长鹏:上周两个国家的高级官员将加密货币称为“硬通货” Re7 Lab
-
特朗普宣布向全民发放 2000 美元“关税红利”,高收入群体除外
贝森特暗示这笔款项可能以免税政策等多元形式兑现。作者:金十数据美国总统特朗普上周日宣称,将向除“高收入人群”外的所有美国人发放“每人至少2000美元的红利”,并表示美国因其关税政策已成为富裕国家。“反
-
加密早报:参院已有足够票数通过结束停摆法案,本周 APT、LINEA、AVAX 等代币将迎来大额解锁
FTX 第四轮偿付预计在 2026 年 1 月进行,分发资格截止确认日期或为 12 月。作者:深潮 TechFlow昨日市场动态消息人士:参议院已获得足够多民主党议员的支持票,以通过结束政府停摆的法案
-
 LuBian 矿池遭黑客攻击被窃取巨额比特币事件技术溯源分析报告
LuBian 矿池遭黑客攻击被窃取巨额比特币事件技术溯源分析报告作者:国家计算机病毒应急处理中心2020年12月29日,LuBian矿池发生一起重大黑客攻击事件,总计127272.06953176枚比特币(当时市值约35亿美元,现市值已达150亿美元)被攻击者窃取
-
 为什么加密市场情绪突然变得如此悲观?
为什么加密市场情绪突然变得如此悲观?原文标题:Why Did Crypto Sentiment Get So Bearish? 原文作者:Jack Inabinet,Bankless 原文编译:Peggy,BlockBeats编者按:在
-
 宏观解读:鲍威尔的“浓雾驾驶”与金融“饥饿游戏”
宏观解读:鲍威尔的“浓雾驾驶”与金融“饥饿游戏”原文标题:"Driving in Fog” and the Financial Hunger Games 原文作者:@arndxt_xo 原文编译:叮当,Odaily 星球日报大幅回调与量化宽松(QE
-
 DeFi 的自然选择:适者生存
DeFi 的自然选择:适者生存作者:cryptographic 编译:Block unicorn前言 自然是冷酷无情的,它没有情感,没有感觉,没有依恋,它只进行着一场永无止境的考验:这种设计是否值得生存。 金融市场亦是如此,随着时
-
MEET48:从造星梦工厂走向链上奈飞 —— AIUGC 与 Web3 重塑文娱经济
Web3文娱正从泡沫退潮迎来重启时刻,以MEET48为代表的项目正通过AI Web3 UGC技术融合重塑内容生产与价值分配范式,构建可持续代币经济体系,从应用走向基础设施,致力成为"链上奈飞"并推动W
- 成交量排行
- 币种热搜榜
 OFFICIAL TRUMP
OFFICIAL TRUMP Pepe
Pepe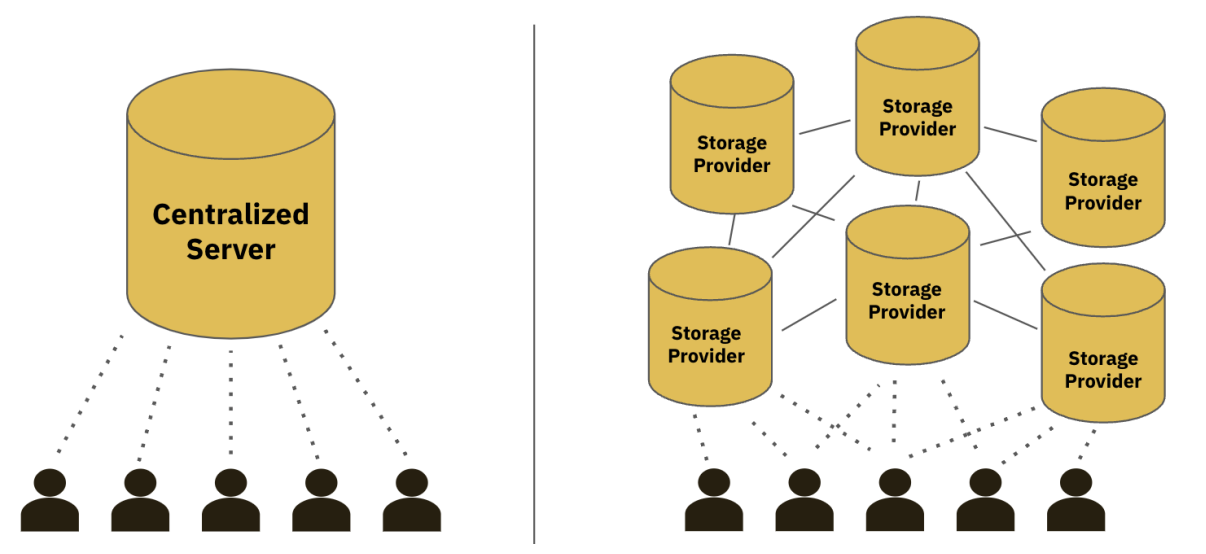

 泰达币
泰达币 比特币
比特币 以太坊
以太坊 USD Coin
USD Coin Solana
Solana 大零币
大零币 瑞波币
瑞波币 First Digital USD
First Digital USD 币安币
币安币 Filecoin
Filecoin 狗狗币
狗狗币 Internet Computer(Dfinity)
Internet Computer(Dfinity) 达世币
达世币 ZEN
ZEN AR
AR OKB
OKB BSV
BSV ETC
ETC EOS
EOS MINA
MINA CFX
CFX